Have you ever been involved in a phone call where the call quality dropped and then came back? This is a rather annoying VoIP issue. This issue is caused by network flickering and packet loss. Troubleshooting VoIP can be quite troublesome at times, even for an IT professional. But the good news is that anyone can fix the causes of network congestion. Soon you can also enjoy phone calls with crystal-clear sound quality. It is also important especially when it comes to Business VoIP Phone Systems.
What is a network jitter?

Network flickering is when a connection causes inconsistent delays between data packets. Unlike packet loss or ping times, the vibration state measures the stability of the connection. The vibration state also affects online activities due to two-way and real-time communication. Examples include online gaming, conference calls, IP security cameras, and more.
When packets arrive at different intervals, the fluctuations cause the sound packets to drop. Vibration issues can affect any network connection. But end users usually experience this problem more over Wi-Fi.
As you know, phone calls that use VoIP are also included in packet delays. Jitter VoIP, on the other hand, manifests itself in phone calls instead of watching a YouTube video. It’s also a good idea to brush up on network connection terms to better understand vibration.
Networking fundamentals
There are some bases in the provision of network communication. These are as follows:
Data Packets
Data packets are the most important part of reliable internet communication. Packets from smaller chunks of a larger message. Packets are needed for the speed and reliability of networks and the Internet as a whole. You have many computers on a network. That’s why huge chunks of data can slow anyone down. Packages help everyone get information reliably.
Data packets include:
• Source and destination IP addresses and ports
• Sort and number of packages
• Protocol information with checksums
• IP phone signal and call status
• Hardware address information
• Optional VoIP QoS headers
About VoIP traffic, phone calls can be converted into voice packets in as little as milliseconds. To achieve this, VoIP also uses various transport protocols for optimal performance.
Transport protocols
When packages are examined, you can see that they are neither reliable nor unreliable. Applications use UDP and TCP to reach their destinations quickly and reliably.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP): Used to reduce round-trip time in the time it takes to send and receive data. The principle here is that applications are responsible for maintaining reliability and even supervision.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): A technology that can be used in less urgent communications. The two devices also confirm that each data packet has been received. If necessary, it will resend the missing ones. It also forms the basis of why VoIP services experience flickering and connectivity issues.
Network congestion, prioritization
Routers have a great role to play in supporting today’s bandwidth-heavy needs, such as video calls. By default, routers help separate the Wide Area Network (WAN) from your local network.
This hands-on approach is good for everyone watching YouTube, streaming music, and participating in video conferencing. But don’t forget to connect your computer and all your devices that are connected to Wi-Fi to Wi-Fi as well. Routers also prioritize traffic from specific devices and traffic classes. This strategy is also referred to as Quality of Service. Its application is also extremely simple. The basic idea here is to allocate bandwidth for VoIP and video conferencing and Real-Time Protocol (RTP) packets.
VoIP, bandwidth, and jitter
Every packet is important because VoIP can convert audio into data packets. Packet delays can also cause gaps in speech and decreased sound quality. A package doesn’t always go directly from your desk to a VoIP service provider.
Network congestion as you consume bandwidth leads to queue delays. This results in even higher latency. Data packets must be reassembled by the recipient. This, in turn, contributes to the amount of vibration. Jitter is also prone to VoIP problems because people can detect delays that are over 500 milliseconds. Depending on the level of tremor, the sound may be choppy or incomprehensible.
How jitter affects VoIP call quality
There may be some network flickering on all internet connections. This is quite normal. It’s also possible that you’ll experience much higher latency during business hours between your office and your VoIP service provider. Package latency variation can also affect your customer communications and conference calls. Especially if some parts of your speech come in a different order, this will affect your speech.
If you don’t have to shake, the phone calls have excellent sound quality. High-definition VoIP codecs such as G.722 and G.729 offer greater accuracy and clarity in VoIP calls. If you have a high vibration, the sound quality of phone calls and video conferences will also decrease. These applications use a very large number of data packets. At the same time, if packets are slow, routers leave them.
How much jitter is acceptable?
Vibration for VoIP measures changes between packet delays for voice communication. The measure of this is expressed as milliseconds or 1% of the second. Generally, the tremor in voice traffic should not exceed 30 milliseconds. For example, your internet connection reached your VoIP provider in 150 milliseconds. If you consider a vibration metric of 30 milliseconds, it reflects a variance of 20%.
The level of vibration that is acceptable also depends on the severity of call quality issues. The question of whether it is temporary or affects many people is very important. Also, note that network vibration is not a one-way street. Delays usually cover both sides of a conversation. This will cause people to talk to each other. At the same time, packet delay variation is a symptom of other annoying network connectivity issues.
To isolate local VoIP quality issues as well, vibration needs to be measured from multiple points. At the point of entering the problem, it is necessary to examine both paths for network congestion.
Ways to test for network jitter
There is no single vibration test that fits everyone. But there are useful uses you may need in your toolbox. Note that vibration can also measure the variation of your network latency. Because it is also measured in milliseconds, network diagnostic tools will help you effectively enter the problem. You can measure your vibration amounts by trying a few different tests.
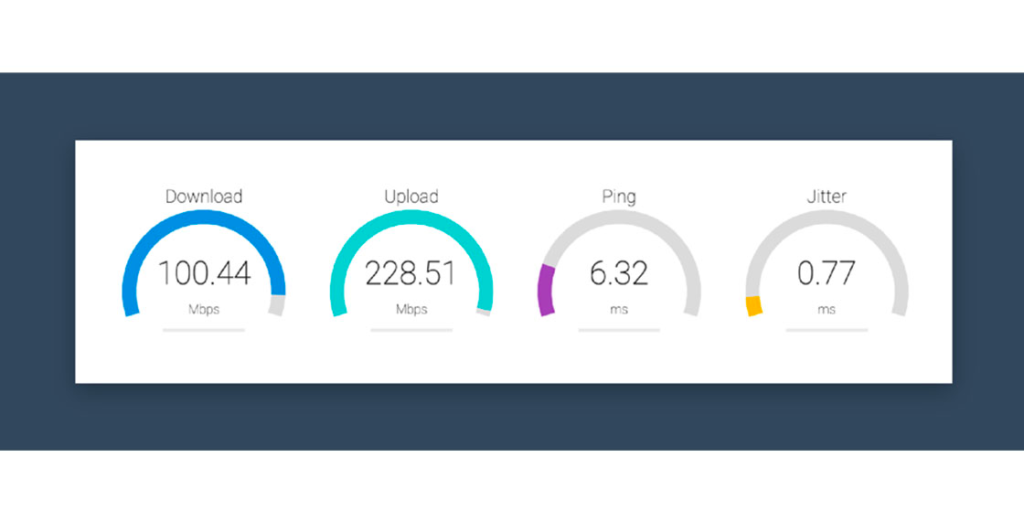
Online speed tests
Bandwidth tests don’t always tell you the full story. It also gives you clues about problems with your internet connection. You can also confirm issues such as bandwidth packet loss and latency in seconds.
Terminal-based ping tests
Browser-based tests can give you a misleading view of your network congestion. VoIP calls, on the other hand, depend on a low-latency connection to a specific VoIP server. You can open a terminal and perform manual ping tests. This command shows you the speed at which each packet must reach that network.
Note also the “mdev”, i.e., maximum milking value. You must make sure that you verify that there is zero packet loss. Instantaneous twitch measurements also reveal which upstream or downstream pathways are problematic. Testing from many endpoints will reveal real-world packet latency variation.
Advanced network monitoring tools
For larger organizations, you may have access to robust network identification tools. This shows the tools working by monitoring all incoming and outgoing traffic at the router level as well. It analyzes all kinds of traffic coming from different endpoints, including SIP Trunk traffic.
How to fix jitter (troubleshooting tips)

The good news for you here is that you can quickly reduce vibration and delay. For optimal call quality, VoIP calls should have a maximum of 30 ms flickering and 100 Kbps bandwidth.
Your approach should also be to identify the root cause of high latency. Setting up VoIP QoS will only get you to one point. The first step is to turn your existing network equipment, including the modem, off and on. In general, this method helps in resolving temporary VoIP flickering issues.
Use a wired internet connection.
Wi-Fi calling can also be vulnerable to interference from microwaves and electric motors. Upgrading existing ethernet cables to category 6 cables can also eliminate faulty wiring. In addition, twisted pairs with superior are also resistant to interference. They support low-latency gigabit speeds.
Disable packet inspection-based firewalls.
Firewalls that analyze your voice packets can contribute to latency on a network. These barriers also control every frame within a package. In an application that is sensitive to speed, such as VoIP calling, these bottlenecks can be picked up.
You need to be configuring your router to perform simple tasks. Broadband network gateways can slow down because they take on too many tasks. Consider enabling Continuous Forwarding (CTF) to also speed up local network performance.
Set up a jitter buffer.
If there are constant amounts of vibrations, it is possible to set a buffer to accommodate the vibration. Vibration buffering also works by delaying VoIP audio sufficiently to accurately reorder audio packets. It can also be too much buffer and it can be difficult to keep track of your calls.
Enable Quality of Service (QoS).

Many businesses also find that their networks are flooded with non-voice traffic. The availability of VoIP phones and access to VoIP networks can also be limited. You can also schedule large data transfers outside of business hours to eliminate packet prioritization concerns.
To get the highest priority, also make sure to assign all VoIP traffic. You can prioritize DSCP class 46, which has the highest priority. QoS also does not harm the download speed. Ensures that voice traffic is not queued.
You can use up to 85% of the bandwidth from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to leave overhead space.
Increase your WAN network bandwidth.
If all methods fail, you probably want to change WAN providers as well. You can also opt for a fiber optic connection for the lowest latency. This step is usually the least preferred option. But it provides a valuable upgrade. You can then adjust the quality of service for VoIP.
It is important to check with your VoIP provider to analyze your network configuration. Some fixes can be as simple as a firmware upgrade on certain VoIP systems. Disabling SIP ALG has little to do with VoIP vibration. But still, it is very advisable to apply it.
Easy and reliable VoIP calls ahead
VoIP technology is an advanced technology over the last 20 years. More than nine out of 10 people have easy access to a broadband connection. Today, nine out of 10 people have access to an excess broadband connection. Smartphones have extremely fast connections like 4G and 5G.
Virtual phone systems come to you right out of the box for maximum performance. You will be able to connect quickly.



